MohrkeCBDReceptors.jpg
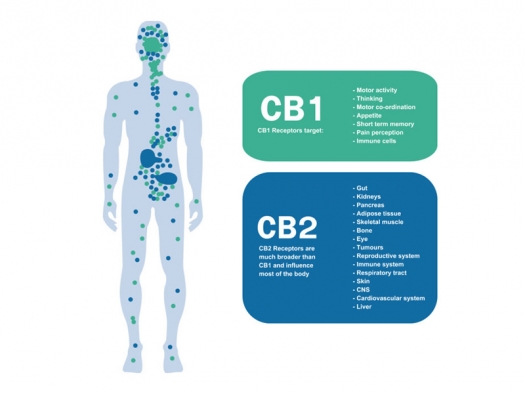
Image courtesy of Martin Möhrke
As soon as we browse through any magazine or surf on Internet and Facebook pages, we can hardly avoid advertisements for cannabis or hemp products that contain CBD. Why are so many companies interested in cannabis lately and are they bringing more and more CBD and other products containing cannabinoids onto the market? Is this only a temporary fad or the beginning of a desirable medical development?
The cannabis plant has a more than 5,000 year old history. In the meantime, there are several thousand varieties and breed crossings of the former primordial plant – breeds that should achieve the highest possible THC or CBD content of these plants. On the one hand to extract intoxicants from it, on the other hand to produce medically effective oils from it.
Medical research never stands still in principle, but never before have so many studies been started on the ingredients of the cannabis plant as in recent years. In the medical meta-database PubMed we find thousands of peer-reviewed studies, scientific papers reviewed by independent experts, in which different mechanisms of action of different cannabinoids are described.
In the Netherlands, for example, recent studies have made a very important discovery that has really amazed researchers: the inflammasome, a protein complex in white blood cells that triggers inflammatory reactions to combat diseased or abnormal body cells, has been reduced by more than 30% by the addition of CBD, thus delaying cell death by up to 64 times the usual time.
Researcher Ronald Glas, who passed away in April 2019, spent over 30 years studying cannabinoids, leaving more than two gigabytes of data and several patents on newly found cannabinoids and combinations of these substances, which he subsequently tested on countless patients.
Further substances are currently being tested on volunteers in placebo-controlled studies. Soon we will see how effective these cannabinoid combinations will be.
Cannabis – a combination drug
It is a widespread misconception that the effect of cannabis products is due only to THC. Rather, the specific effects of certain types of cannabis plants are caused by the combination of several cannabinoids such as CBDV THCV, CBG, CBC, CBD, CBN and other unspecified cannabinoids and terpenes, which also occur in different concentrations in the plants. That is why every type of cannabis is unique in its medical and recreational effect.
What are cannabinoids and what do they do?
Cannabinoids are active substances which are mainly found in the plant species Cannabis sativa with its subspecies C. indica and C. ruderalis. They have strong pharmacological effects in virtually every signal transmission system of the central and peripheral nervous system as well as the immune system of our body. In fact, all immune cells have so-called CB receptors on their surface.
It is a coincidence of evolution that the cannabinoid THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) contained in the cannabis plant bears a strong resemblance to the endo-cannabinoids naturally occurring in the human body, such as anandamide (AEA). Therefore, both molecules can interact with the recently discovered CB1 and CB2 receptors located on corresponding body cells. Just like a key in a lock, both substances fit perfectly into these receptors and, in this docking maneuver, ensure corresponding reactions in the cell itself. For example, in the case of nerve cells, the alteration of neuronal action potentials is accomplished.
These endo-cannabinoids, such as anandamide, and therefore also THC (!) are involved in such important key processes of the body as eating, sleeping, forgetting (trauma) and protecting (by strengthening the immune system). They regulate the entire brain-intestinal-axis, which is currently a very popular target for the pharmaceutical industry, which wants to combat obesity successfully.
CB1 receptors have recently also been found on the glial cells of our nervous system. This explains the successful pain relief in neuropathic disorders after administration of a cannabis product containing pure THC (used as a painkiller) but through combinations that are possible with other cannabinoids we are able to make other painkillers for example with euphoric or for insomnia, therefore again combination drug. In the meantime, more than 120 identified cannabinoids and more than 400 other substances have been isolated from the cannabis plant. These are to be found almost exclusively in the female form of the hemp plant. The male form of the plant serves the industry – mainly for the production of paper, in former times also for the production of hemp ropes – but it is not suitable for medical purposes, although science is not certain about this yet. However male plants are also important for example to develop new sub-chemotypes.
Endo-Cannabinoids – Neurotransmitters in our body
Endo-cannabinoids are the body's own active ingredients and belong to the neurotransmitter system of our body. The receptors in this system work very close together with these neurotransmitters and external cannabinoids from the cannabis plant as described above – for example THC with the receptor CB1 and CBD with the receptor CB2. These receptors are protein complexes on or in the cell membrane of body cells. If a THC molecule from the bloodstream adheres to such a CB1 receptor – for example a brain cell – this triggers a change within the cell, which then runs along the nerve pathways as an excitation potential, before finally being passed on to the immune system, where corresponding defense cells then take action.
There are hundreds of different receptors found on all types of cells in our central nervous system (brain) and peripheral nervous system (body). The CB1 and CB2 cell surface receptors are only the most frequently occurring receptors in the body, both with regard to the number and presence in the organs (brain, smooth muscle tissue, sexual organs, digestive organs) and the immune system (B-cells and T-killer cells). These two receptors are universally involved in the transmission of nerve impulses by almost all known neurotransmitters.
Externally added cannabinoids compete with these transmitters for these CB receptors, triggering effects similar to those of the body's own transmitters.
For example, CBG, cannabigerol, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in various cannabis species, is similar to the body's neurotransmitter GABA and can therefore, like GABA, promote sleep and positively affect some hypothalamic nuclei that cause anxiety.
However, the various external cannabinoids influence the activity of almost all of these transmitting substances in the brain: not only GABA, but also dopamine, acetylcholine, endorphins, prolactin, glutamate, histamine, noradrenalin, prostaglandins, serotonin and opiodpeptide and many others. This explains why cannabis products can have a positive effect on so many diseases.
However, this positive circumstance also holds a danger: If we use a natural cannabis oil with its many different cannabinoids, we can hardly predict which reaction this oil triggers in the body.
This is why we are increasingly adding separately isolated cannabinoids in high doses to the oils in order to be able to help the patient in a specific way. For example, an oil with a high CBD content is recommended if a healthy sleep is to be achieved (calming down) or a healthy bone formation – or if fears have to be reduced. This is not always the case with each patient. There are other cannabinoids which have a much more efficient effect for fighting insomnia or bone forming then CBD like CBG for example. But there are combinations with 3 combinations which are even more effective than only a single cannabinoid like CBD.
Practice shows that we can alleviate many complaints in this way. CBD products and products containing other cannabinoids are now available almost everywhere, but often of very different quality. We'll have to come back to that later.
In combination, cannabinoids may have both synergistic and antagonistic or additive effects with respect to their two-phase and bidirectional effects. This is what makes the activity of "medicinal marijuana" so complex and profound: a powerful, gradually sedating effect, an effect on appetite, a strong sleep stimulation ("narcotic") – or quite the opposite, a strongly stimulating, activating effect. And all this by the cannabinoid THC alone. What makes "medical marijuana" an analgesic, an antiemetic and a spasmolytic product in one.
Cannabis in geriatrics
Due to their proven safety, some specific marijuana simplex preparations that evoke strong analgesic and euphoric effects are well suited for palliative and geriatric treatment. They increase mood and well-being, increase the appetite and ensure a good night's sleep.
The following cannabinoid formulations are equally capable: pure substances, hemp oils, biscuits, teas (as a colloid solution without formation of deposits) – all with appetite-stimulating and mood-enhancing properties.
CBD against anxiety and tension
Studies show that CBD has a very strong effect on nerve cells, axons and dendrites and can sometimes heal them again: The nerve connections are restored and receptors can then communicate with each other again. This is why a number of psychosomatic complaints can be demonstrably alleviated with CBD products: Anxiety, pain and tension.
CBD is also the first non-toxic exogenous substance that can significantly reduce the expression of ID-1 in metastatic breast cancer cells, leading to a reduction in tumor aggressiveness. ((Mol Cancer Ther 2007;6(11):2921-7))
CBD models THC effect
Animal studies show that pre-treatment with CBD increases THC levels in the brain. This is because CBD, which acts as a competitive inhibitor of cytochrome P450, slows down the conversion of THC into its stronger metabolite 11-OH-THC. As a result, THC remains active longer, but does not reach its normal maximum effect.
Anyone who is acutely or permanently under stress will notice how the tension in the body is released within just a few minutes after taking CBD drops. People with hands sweating with fear are calmer after 3 to 5 minutes (measurable). However, one must not forget to eliminate the triggers of stress or fear in the environment. Emotional problems, toxins or hypothalamus disorders can also be the cause of various problems and disorders.
Measurements in our practice and blood tests in the laboratory prove the effectiveness of CBD drops. We can also distinguish between acute and chronic stress with HRV (heart-rate variability) measurements.
In the figures below we show measurements from a patient who suffers from acute stress and who is very nervous. If we examine the initial state of the sympathetic nervous system, it is clearly overactive (it should be in the area of the green rectangle). As soon as we administer 3 drops of CBD by mouth and take another measurement after a few minutes, we can see how a healthy state of equilibrium is restored.
This positive result can be seen regularly in our practice, and we notice that in the stress-free constitution thus created, every additional therapy works better and faster. Therefore, we advise every patient to take CBD drops before starting therapy and we combine the long term therapy often with a Rhodiola Rosea root extract of 400 mg. This combination has a very good effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Another very interesting discovery was that CBD very successfully draws the heat from the lymph. This can be shown very well with an infrared screening image (thermography).
Even if we directly analyze living human blood and add the purest CBD to the blood, we can see that the inflammatory values immediately decrease and the swelling of cells is reduced up to 30%. Scientists are so enthusiastic about this that they started another study.
Currently much is being written about the effects of CBD, but many of the indications described have often not been substantiated or proven by manufacturers with measurements. Many further observations, investigations and studies must therefore follow. Nevertheless, CBD is a promising substance for the future that we simply cannot ignore. Unfortunately, at the moment, the pharmaceutical industry and the European authorities are doing everything they can to classify CBD as a drug. This would mean that it would lose its current status as a food- or dietary supplement.
CBD products under fire
CBD has probably become so popular because it can easily replace many conventional drugs. That's why more and more organizations are suing CBD, and payment providers like PayPal are blocking all CBD and cannabis product sales in Europe. Unfortunately, EFSA, the European Food Safety Authority, has also wrongly put all cannabinoids on the Novell Food List, although cannabinoid products were already on the market before 1997. Most cannabis products have now been removed from display at the Pharmacy Museum in Heidelberg, and only a showpiece bottle and a few old seeds are on display. Are these active substances slowly being snatched away from us and only provided to the pharmaceutical industry?
Cannabinoids are, from a pharmaceutical point of view, a group of harmless medical substances that differ significantly from synthetic artificial drugs such as barbiturates, benzodiazepines, imidazopyridines and many other types of sedatives. But, for example, they lacked long-term experiments with these substances.
So where will the cannabis case go in the future? Will THC remain in the illegal grey area? It is estimated that over 5 million people use CBD, only in the EU already. In Austria it is now prohibited and all BIO certifications have been withdrawn. At this moment most Austrians therefore order CBD-products in Germany or other countries.
Nevertheless, cannabis and cannabis products can confidently be predicted to have a golden future. In the meantime, researchers are working on other previously unknown components of the cannabis plant and are identifying more every day. Many countries are releasing cannabis, other countries want to follow this example. Even the smoking of joints or “vaping” of cannabis where there is no burning, or the use of super distillates of various cannabinoids is to be given a place in medicine in the future. At this moment, oils may not contain more than 0.2% THC. Most are made from hemp oil from the Cannabis sativa, which naturally contain a little bit of THC. Although they contain a number of different substances, they have a much smaller effect than the cannabis products from other original cannabis plants. For example, hemp oil contains 0.0001% THCV and other plant parts up to 0.3%. Today, through new cross-breeds and newly patented technologies, specific cannabinoids can be concentrated very highly and a mixture of the most diverse and important cannabinoids can be produced, the effects of which are known. If only 5 out of 200 conceivable substances are still in the end product, the effect of the product and the interactions with conventional medicines can still be assessed well.
In principle, however, the CBD content should never be higher than 10%. In this way, CBD can never be overdosed, even if blood thinners or thyroid medications are taken whose effects may be affected by CBD. CBD ensures that toxins – but also drugs – are removed from the blood more quickly, which would not be desirable in the case of certain drugs. In principle you cannot get an overdose of CBD or THC what a lot of people think. You can feel very uncomfortable but this is dedicated to the “status and current wellbeing” of the patient at that moment. Panic attacks can happen for example with the use of THC but usually this is over after 1-2 hours and will not give any damage like conventional medicines.
But those who take a cheap hemp oil with about 200 ingredients, the effects of which are not yet clearly known, take a certain risk. For the time being, it is even better to take various cannabinoids separately, or a combination of them, whose interactions with conventional drugs are known. Another problem is the mixture of CBD and THC, which is very suitable for cancer therapy, but at the same time has an intoxicating-stoned making effect. Thanks to the findings of medical research, such improvements will become even faster and more numerous in the future. The reservoir of potentially effective cannabinoids appears to be at least almost inexhaustible.
If the patient is able to find the right cannabis product for his symptoms, the best possible effects will undoubtedly be achieved.
For more information, visit Optima Health.


