OzoneHowMade.jpg
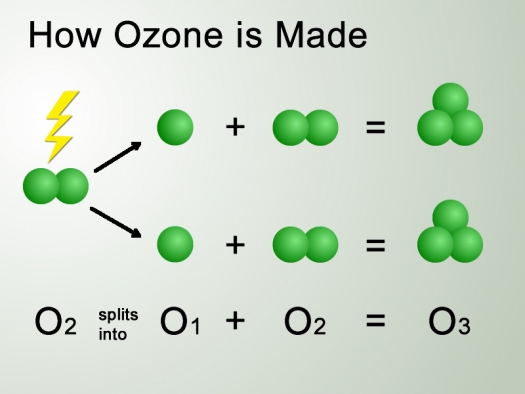
Image by FAIM, ©2016
Ozone is made when an energy source splits oxygen (O2) into two O1 molecules. Each O1 molecule then joins an O2 molecule to form ozone (O3).
Oxidative Therapy involves treating the body with extra oxygen. There are several treatment methods including mixing the blood with ozone gas (O3 instead of the O2 we breathe), injection of ozone under the skin to treat scarring, insufflation into the rectum, bladder, vagina, ear, and nose, and forcing additional oxygen gas (O2) into the lungs under pressure (hyperbaric oxygen). This addition of extra oxygen has many benefits for both prevention and treatment of disease.
Oxidation is an extremely important energy-producing chemical reaction in the body using various forms of oxygen but it must be used carefully by trained professionals to prevent oxidative damage to the tissues. However, there are some treatments that can be done at home with proper training and quality equipment.
Research has found that the immune system uses the energy from oxidation to destroy bacteria, virus, yeast and parasites. Ozone therapy is a unique form of therapy that both heals and detoxifies at the same time. It is used for a variety of chronic disease including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, Lyme disease, chronic hepatitis, herpes, chronic fatigue states, chemical sensitivity, macular degeneration, chronic bladder conditions, colitis, auto-immune diseases, Crohn’s disease, as well as pain conditions. The most common delivery of ozone is major autotherapy hemotherapy (MAHT) where ozone is delivered via IV, and in most cases the most effective way ozone is administered.
Hyperbaric oxygen is commonly used in hospitals for wound healing, but it has so many more broad reaching applications. Please see Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for PTSD and Brain Injuries for more information.
Often times ultraviolet blood irradiation (UBI) therapy is combined with other oxidative therapies with good results. For more information visit This Is the Only Solution for Antibiotic-Resistant Superbugs.
Many believe that the use of oxidative therapy is the wave of the future in the treatment of resistant bacteria which have resulted from the overuse of antibiotics in people and animals.


